Heart Attack Types Explained: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Heart Attack Types Explained: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
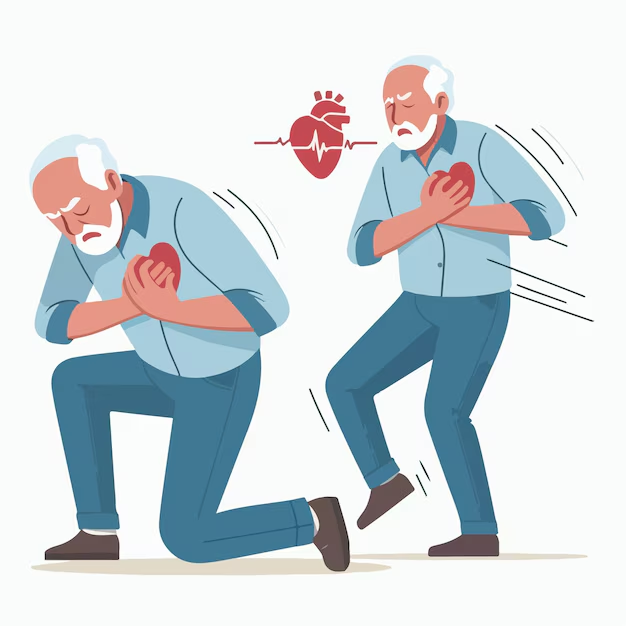
A heart attack is a medical emergency that occurs when blood flow to the heart is severely reduced or blocked, leading to damage or death of heart muscle tissue. Understanding the different types of heart attacks, their causes, symptoms, and treatments can help you recognize warning signs early and seek timely medical care.
What Are the Different Types of Heart Attacks?
Heart attacks are medically referred to as myocardial infarctions (MI). They are classified into different types based on their causes and severity:
1. ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI)
- What Happens? A complete blockage of a coronary artery, cutting off blood supply to a part of the heart.
- ECG Findings: Elevated ST segment (visible on an electrocardiogram).
- Severity: Most dangerous type, requiring immediate treatment.
2. Non-ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI)
- What Happens? A partial blockage of a coronary artery, reducing blood flow but not completely stopping it.
- ECG Findings: No ST elevation, but other changes like T-wave inversion may appear.
- Severity: Less severe than STEMI but still requires urgent care.
3. Coronary Artery Spasm (Silent Heart Attack or Prinzmetal’s Angina)
- What Happens? Sudden tightening (spasm) of a coronary artery, reducing blood flow.
- Symptoms: Can occur at rest, often mistaken for indigestion.
- Risk Factors: Smoking, stress, and drug use (e.g., cocaine).
4. Demand Ischemia (Type 2 MI)
- What Happens? The heart needs more oxygen than the body can supply (due to fever, anemia, or rapid heartbeat).
- Common in: Patients with chronic illnesses like diabetes or kidney disease.
What Causes a Heart Attack?
The primary cause is coronary artery disease (CAD), where plaque (cholesterol deposits) builds up in the arteries. Other causes include:
- Blood clots blocking an artery
- Artery spasms (due to stress or drugs)
- Severe blood loss or low oxygen levels
- Risk factors: High blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, obesity, family history, and sedentary lifestyle.
Heart Attack Symptoms: Don’t Ignore These Signs!
Symptoms vary, but common warning signs include:
✔ Chest pain or pressure (feeling like an elephant sitting on your chest)
✔ Pain spreading to the arm, neck, jaw, or back
✔ Shortness of breath
✔ Cold sweats, nausea, or dizziness
✔ Fatigue or sudden weakness
Note: Women may experience atypical symptoms like indigestion, extreme fatigue, or back pain.
How Is a Heart Attack Diagnosed?
Doctors use:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) – Detects heart rhythm abnormalities.
- Blood tests (Troponin levels) – Measures heart muscle damage.
- Angiography – Identifies blocked arteries.
- Echocardiogram – Checks heart function.
Emergency Treatment for Heart Attacks
Time is critical! The faster you get treatment, the better the outcome.
1. Immediate Treatments
- Clot-busting drugs (Thrombolytics) – For STEMI if stenting isn’t immediately available.
- Angioplasty & Stent Placement – Opens blocked arteries (primary treatment for STEMI).
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) – For severe blockages (open-heart surgery).
2. Long-Term Management
- Medications: Aspirin, beta-blockers, statins, blood thinners.
- Lifestyle Changes: Quit smoking, exercise, heart-healthy diet (low salt, low fat).
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Supervised exercise & education for recovery.
Can You Prevent a Heart Attack?
- Control blood pressure & cholesterol
- Manage diabetes & weight
- Exercise regularly (30 mins/day)
- Eat a balanced diet (fruits, veggies, whole grains)
- Avoid smoking & excessive alcohol
Final Thoughts
A heart attack is a life-threatening event, but recognizing symptoms early and seeking prompt medical help can save lives. If you or someone experiences chest pain with other warning signs, call emergency services immediately.
Stay heart-healthy!