Introduction
If you’ve been advised to undergo EPS + RFA, you may be wondering what these terms mean. This blog explains the procedure in simple language — what it is, why it’s done, benefits, risks, and recovery tips
What Is an EPS RFA Procedure?
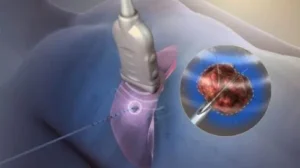
1. EPS (Electrophysiology Study)
An EPS is a specialized test that studies the electrical system of your heart.
Doctors insert thin wires (catheters) into your heart through a vein in your leg or neck to check:
- Why your heartbeat is irregular
- Which area of the heart is causing abnormal rhythms
- Whether you need ablation, pacemaker, or ICD
EPS helps diagnose conditions like SVT, VT, WPW syndrome, Atrial flutter, Atrial tachycardia etc.
- RFA (Radiofrequency Ablation)
If EPS detects an abnormal electrical pathway, the doctor immediately performs RFA to treat it.
How RFA works:
Gentle radiofrequency energy (heat) is applied to the tiny portion of heart muscle causing the irregular rhythm.
This:
- Blocks the faulty electrical circuit
- Restores normal heart rhythm
- Prevents future episodes
RFA is a permanent cure for many arrhythmias.
2.Why Is EPS RFA Done?
Doctors recommend this combined procedure for:
- Recurrent palpitations
- Rapid heartbeats
- Fainting episodes
- SVT & AVNRT
- WPW syndrome
- Atrial flutter
- Certain ventricular arrhythmias
3 Benefits of EPS RFA
- 95–98% success rate in common arrhythmias
- Immediate improvement
- Minimally invasive
- No open surgery
- One-day hospital stay
- Reduces or stops medications
- Long-term cure
- 4.Risks & Side Effects
Though very safe, minor risks may include:
- Bruising at catheter site
- Mild chest discomfort
- Rarely bleeding or infection
- Very rare: heart block requiring pacemaker
- Recovery & Aftercare
- Rest for 24–48 hours
- Avoid heavy lifting for 1 week
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Follow up in 1–2 weeks
- Take medications as advised
What’s the Latest in CRT-D? 2025 Breakthroughs Patients Should Know
Introduction
CRT-D (Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy – Defibrillator) is a life-saving device for patients with heart failure and dangerous arrhythmias.
Recent advancements in 2024–2025 have made CRT-D smarter, smaller, and more efficient. Here’s what’s new.
1. Endovascular (Leadless) LV Pacing – HOTTEST TREND
Companies like Medtronic & Boston Scientific now offer:
● Leadless LV pacing systems
● No need to place a wire in coronary sinus
● Ideal for patients with difficult anatomy
● Lower complications & better response
2. Multipoint & Multisite Pacing
New CRT-D models can pace the left ventricle from multiple points simultaneously.
Benefits:
● Greater heart pump efficiency
● Higher responder rates
● Reduced HF hospitalizations
3. Artificial Intelligence in CRT-D
Modern CRT-D devices can:
● Self-adjust pacing settings
● Predict arrhythmias
● Detect heart-failure worsening early
● Send alerts to your doctor’s mobile dashboard
● Provide real-time remote monitoring
This leads to faster treatment and increased survival.
4. Smaller, Longer-Lasting Batteries
2025 devices come with:
● 10–14 years battery life
● Smaller, thinner device size
● More comfortable for young and elderly patients
5. MRI-Safe CRT-D
Nearly all new CRT-D devices are MRI-compatible, allowing patients to undergo scans safely when needed.
6. Bluetooth + Smartphone Connectivity
Patients and doctors can now view:
● Device status
● Heart rhythm
● Battery life
● Alerts
All through secure mobile apps.
Who Needs a CRT-D?
● Severe heart failure (EF < 35%)
● Left bundle branch block
● Wide QRS
● Recurrent ventricular arrhythmias
● High risk of sudden cardiac death
● Non-responders to old CRT technology