Difference Between Heart Attack and Sudden Cardiac Arrest

Difference Between Heart Attack and Sudden Cardiac Arrest

Many people use the terms heart attack and sudden cardiac arrest interchangeably, but they are two different medical emergencies. Understanding the difference can save lives, as each condition requires a unique response.
In this blog, we’ll break down:
✔ What is a heart attack?
✔ What is sudden cardiac arrest?
✔ Key differences between the two
✔ Warning signs and symptoms
✔ How to respond in an emergency
What is a Heart Attack?
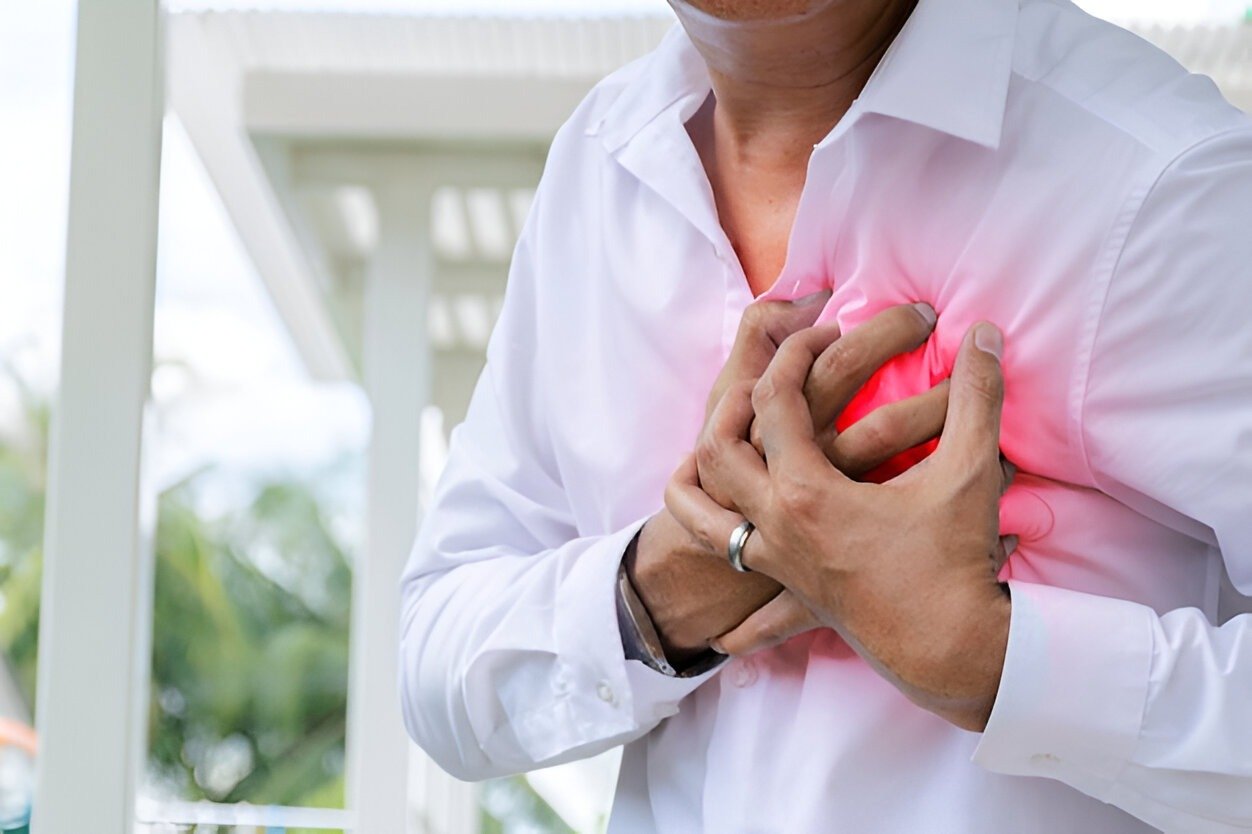
A heart attack (myocardial infarction) occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, usually due to a clot in a coronary artery. Without oxygen-rich blood, the heart muscle begins to die.
Symptoms of a Heart Attack
- Chest pain or discomfort (pressure, squeezing, fullness)
- Pain radiating to the arm, neck, jaw, or back
- Shortness of breath
- Cold sweat, nausea, or lightheadedness
Important: Symptoms can develop slowly (over hours or days) and vary between men and women.
What is Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA)?
Sudden cardiac arrest is an electrical malfunction in the heart that causes an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), stopping blood flow to the brain and body. Unlike a heart attack, SCA leads to immediate loss of consciousness and death within minutes if not treated.
Symptoms of Sudden Cardiac Arrest
- Sudden collapse
- No pulse or breathing
- Loss of consciousness
- Gasping or no breathing at all
Key Differences Between Heart Attack and Cardiac Arrest
| Factor | Heart Attack | Sudden Cardiac Arrest |
| Cause | Blocked artery (blood flow issue) | Electrical malfunction (heart rhythm stops) |
| Consciousness | Usually remains conscious | Immediate loss of consciousness |
| Breathing | Typically continues | Stops abruptly |
| Onset | Symptoms develop gradually | Happens suddenly, without warning |
| Survival Chances | Higher if treated early | Requires immediate CPR & defibrillation |
How to Respond in an Emergency?
For a Heart Attack:
- Call emergency services immediately.
- Chew aspirin (if not allergic) to help thin blood.
- Keep the person calm and seated.
- Do NOT delay treatment—every minute counts.
For Sudden Cardiac Arrest:
- Call for help and start CPR (chest compressions) immediately.
- Use an AED (Automated External Defibrillator) if available.
- Continue CPR until medical help arrives.
Prevention Tips
- Maintain a heart-healthy diet (low salt, low cholesterol).
- Exercise regularly and avoid smoking.
- Monitor blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Learn CPR & AED use—it can save lives!
Final Thoughts
While both heart attacks and sudden cardiac arrest are serious, they are not the same. A heart attack is a circulation problem, while SCA is an electrical problem. Knowing the signs and acting quickly can make the difference between life and death.
If you or a loved one has heart disease risk factors, consult a cardiologist for regular check-ups.
Stay informed, stay prepared, and take care of your heart!